Spotlight on International Charter Data Contributors: NGII
News
26 noviembre 2024
Spotlight on International Charter Data Contributors: NGII
A brief introduction of NGII
Korea's National Geographic Information Institute (NGII) is a national mapping agency under the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (MOLIT) and plays a vital role in establishing the national spatial reference system and formulating national spatial information policies. The NGII provides and services a diverse range of high-quality spatial information, including national base maps, aerial and satellite imagery, and Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), to lead the digital transformation of land management. Furthermore, it develops next-generation spatial information necessary for future growth drivers such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and Urban Air Mobility (UAM), promoting the data economy and spatial information-based industries in the Republic of Korea.
Motivation for participating in the Charter
MOLIT has pioneered high-resolution national land satellites, CAS500-1 and CAS500-2, designed for precise ground observation. These cutting-edge satellites are instrumental in gathering geospatial information, managing land use, and responding to disasters. NGII is entrusted with the operation and utilization of these advanced satellites. NGII's primary goal is to harness the power of these satellites for detailed observation and optimized data usage across the Korean Peninsula. Additionally, to address international challenges that require multinational cooperation, including disaster response, they joined the International Charter: Space and Major Disasters.
The specific types of data NGII provides
The National Land Satellite, known as CAS500-1 and CAS500-2, consists of twin satellites with identical specifications, each approximately 550 kg in weight, operating in a Sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of approximately 500 km. The spatial resolution for black-and-white imagery is 0.5 meters, while the color bands-Red, Green, Blue, and Near-Infrared (NIR)-achieve a resolution of 2 meters. The satellites offer an observation width of 12 km and a radiometric resolution of 12 bits. The first satellite was successfully launched on March 22, 2021, and is currently functioning optimally. The second satellite has completed its development phase and is slated for launch in 2025. Images captured by the National Land Satellite are provided with initial radiometric and orthorectification corrections. For images of the Korean Peninsula, more precise geometric and orthorectification corrections are applied using ground reference points to ensure greater accuracy.
Examples of activations
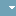
Flood in Libya (Activation 839)
Storm Daniel, a medicane caused by a low-pressure system, resulted in catastrophic flooding in Libya on September 10, 2023, particularly in the city of Derna, where over 4,000 fatalities, more than 10,000 missing persons, and 50,000 displaced individuals were reported, as two aging dams collapsed under heavy rain, unleashing a 7-meter-high wave. The satellite images below show the affected areas in Derna, with both before and after views.
List of contributions
As of November 2024, NGII has contributed data across 11 activations in the following countries:
- Kahramanmaras earthquakes in Türkiye (Activation 797)
- Flood in Libya (Activation 839)
- Flood in the Marshall Islands (Activation 858)
- Cargo ship oil spill in Trinidad and Tobago (Activation 861)
- Flood in Mongolia (Activation 869)
- Cyclone Gamane in Madagascar (Activation 870)
- Flood in Afghanistan (Activation 878)
- Flood in Russian Federation (Activation 882)
-
Kyrgyzstan:
- Landslide in June 2024 (Activation 889)
- Flood in July 2024 (Activation 898)
- Mudflow in August 2024 (Activation 902)

 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French Chinese
Chinese Russian
Russian Portuguese
Portuguese